Psoriasis- One of the most common diseases, the frequency of disease in the population is constantly increasing every year. And if we assume that absolutely all age groups are susceptible to this pathology, and its simple form quickly turns into a more complex form, the question of appropriate therapy and prevention is really very much. necessary.
According to statistics, about 30 inhabitants of the planet suffer from this disease in one degree or another. What to do for people with psoriasis? What medicines and folk remedies can be treated? How to properly organize your meals? In the end let's put all the points.
Psoriasis and its causes
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease with a rather vague etiology - the exact cause, although there is much research in this area, is unknown. It is believed that this pathology is the result of genetically determined changes in the immune system, as a result of which chronic dermatitis develops. However, its multifactorial nature is also not excluded - in other words its relevance, along with its genetics and external influences.
It is noteworthy that the causative factors, according to the scientists, are quite different for different age groups: for example, if the types of bacterial infections are different, including, in particular, associated infections. bridge, which is considered to cause triggers in children, then in adults. Factors that stimulate stress and nicotine abuse are paramount. alcohol, obesity and the use of certain drugs (eg, adrenaline receptor blockers).
It is impossible to completely cure psoriasis, however, modern medicine has the ability to significantly reduce the course of the disease and maintain long-term remission in the patient.
There are several theories to explain the onset of psoriasis:
- infectious and parasitic;
- nerve stimulation;
- Endocrine;
- metabolism;
- Immunology;
- hereditary;
- molecular mimic theory.
As with many other medical conditions, the cause of skin problems should be found in the intestines. Its length is 4 to 6 meters, and the inner surface is covered with villi, the total area of which is equivalent to the size of a tennis court - this allows for efficient absorption. much more. Interestingly, the cells of the mucous membrane of the small intestine are completely renewed every 3-5 days. Furthermore, up to 70% of human immune cells are concentrated here. Therefore, one of the most common causes of psoriasis is considered leaky bowel syndrome (LEPS).
Deviation from the normal functioning of the intestinal mucosa will lead to malabsorption, i. e. a violation of the assimilation of basic nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals). In addition, the negative effect on the body of toxins and allergens increases: under such conditions, they are much easier to enter the bloodstream. The direct link between psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease has been demonstrated in numerous studies.
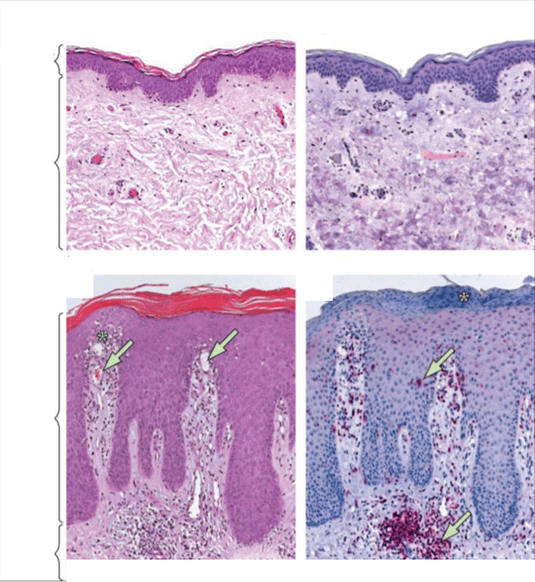
Other studies by scientists confirm that a special microbiome is formed on the skin of psoriasis patients, which is significantly different from that of healthy skin.
In the area of psoriasis lesions, a large mass of bacteria is concentrated, their stability is significantly lower than that of normal skin - especially the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus, which has an extremely negative effect. to the inflammatory process.
Types of psoriasis
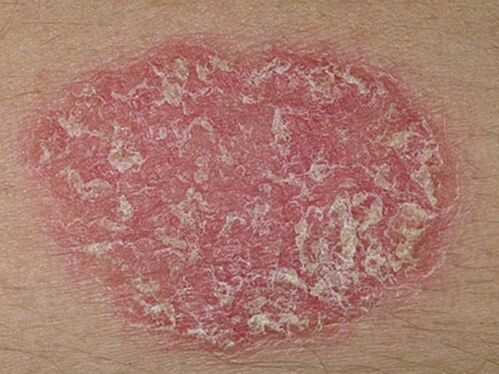
- Plaque psoriasis. . . In 90% of cases, dermatologists face this particular form of the disease, also known as a simple or common disease. First, separate small areas appear on the skin, raised above the level of the healthy dermis. These inflamed areas are called psoriatic plaques. Gradually, they develop, merging with their neighbors into a whole.
- Reversible psoriasis.This diagnosis is made for patients who develop fine red nodules in the folds of the skin and inside the folds - in the groin area, on the inner thighs, under the breast. Unlike pure psoriasis, inflammatory foci are essentially not covered by scabs, but due to their location and constant friction, they cause serious discomfort for the patient. In addition, there is a risk of recurrent streptococcal or fungal infection, because in the localized spots, the high humidity and temperature create ideal conditions for the reproduction of microorganisms.
- Intestinal psoriasis.This type of disease gets its name from the shape of systems. Lesions are in the form of drops, protruding above the level of healing. A common cause for this form of psoriasis is a previous streptococcal infection, as we mentioned earlier. The problem is that the patient's immunity, affected in the fight against infection, is severely impaired - his resources are not limitless, and, like all living things, recovery takes time - and this is due to an autoimmune disease. has been activated.
- Purulent psoriasis.This is considered the most severe form, accompanied by the formation of blisters filled with clear liquid. Dermatitis begins around the foci, swelling and thickening. With a secondary exacerbation, the likelihood is quite high, the blisters are filled with pus. Purulent psoriasis foci are localized in the arms and legs. In difficult cases, there is a common place for blisters on the body, their rapid growth and the risk of infection of the entire skin surface.
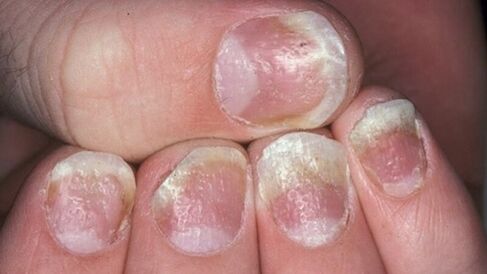
- Psoriasis on the nails.This type of disease changes the appearance and structure of nail plaques on the hands and feet. Nails thicken, lose their natural color, have an unpleasant odor. The skin around the nail is rough, forming thick ridges. In severe cases, the nail may go away without regrowth afterwards.
- Psoriatic arthritis.In this case, the disease affects the joints and connective tissues. Usually, the inflammation affects the distal phalanges of the extremities. There is inflammatory psoriasis - swelling of the fingers. The hip and knee joints also suffer from the devastating effects of the raging illness. There are often cases of disability losing the ability to move independently.
- Psoriatic erythema.Flaky spots appear on the skin, and flaking of the affected layer can be observed. The patient feels extremely uncomfortable due to the itching and constant swelling. Usually, this diagnosis is made for patients who have received simple treatment for psoriasis, but have not completed therapy or have changed medications.
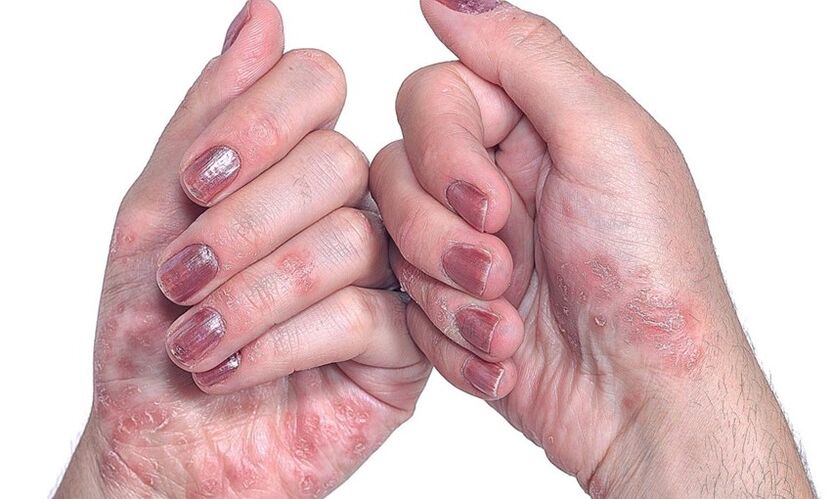

Symptoms of the disease
The first manifestation of psoriasis is a small red rash on the skin. The papules grow rapidly, develop into spots 4 to 8 cm in diameter, they become more and more numerous and form dry scabs on the surface. In severe cases, individual spots fuse together and the damage affects large areas of the body. Psoriasis can be distinguished from other skin diseases by round, well-defined boundaries, bright red or pink, silvery-white scabs. They appear first on those skin areas, their integrity is compromised by abrasions, wounds, frostbite, constant friction. There are three characteristic signs that confirm the onset of psoriasis:
- Stearin spotting phenomenon- The dried seeds readily separate from the affected surface, revealing an area that looks like a drop of wax or sterol.
- Psoriasis phenomenon(end) movie. Further cleaning the papules from the scab allows you to see a transparent, moist film, and the skin underneath is inflamed.
- The Auspitz phenomenon. . . The removal of the end membrane results in the appearance of the smallest blood droplets on the stain surface.
This trio of psoriasis is unique - its presence allows for an unmistakable accurate diagnosis. However, different parts of the body have their own characteristics of the manifestation of the disease.
- Psoriasis on the body.The back, neck, abdomen, thighs and lower legs are most commonly affected by guttate psoriasis. Small, tear-shaped papules grow, emerging on the skin's surface. This form of the disease is most often diagnosed in people who already have a staph infection.
- Psoriasis on hands.The most common locations for the appearance of psoriatic papules on the hands are the elbows and the space between the vertebrae - while as a rule, a form of plaque is observed, in which individual small plaques merge. fused into a single lesion covered with dry scales. The forearms are much less likely to be affected.
- Psoriasis in the legs. It begins with a single rash in the knee area. The inflamed areas disturb the patient with intense itching and peeling, rapidly increasing in size and fusing with the surrounding areas.
- On the palms of the hands and feet.In most cases, the simultaneous defeat of both the palms and the feet is noted, but in some patients the disease affects the horny layer of the upper or lower extremities. Due to the development of psoriatic papules, the skin thickens, becomes rough and cracked further.
- Psoriasis of the scalp.First, the rash appears on the forehead, behind the head, and behind the ears. First, the patient notes that single scaly formations that develop, merge with nearby scales and over time, can affect the entire scalp. The papules are very itchy, thus causing a constant need to scratch the skin - wounds and cracks thus potentially become the gateway to infection. The dried seeds are separated from harmful ingredients - first small, a bit like dandruff, then larger scales.
- On the face, ears, neck.Localization of psoriatic papules on the face is an exception in the common clinical setting. In rare cases, when this happens, the disease affects the areas around the eyes and eyelids, as well as the cheeks and tongue. Formations on the neck quickly spread more quickly - backward or head. The ear is where seborrheic psoriasis develops. Papillae can appear both inside the cartilage and outside. When making a diagnosis, it is important not to confuse the disease with seborrheic eczema, which has similar symptoms.
- On the nails.There are three options for initial manifestations of psoriasis on nail plates. First is the appearance of small indentations. The second is that the nails thicken, changing their natural color to gray or yellow. With the further development of nail psoriasis, the plaque sloughs off, the upper particles easily separate. And, finally, third is the deformation of the foundation, accompanied by a loss of the smoothness of the plate and the appearance of concave areas.
- Symptoms of psoriasis in children.In the early stages, the disease progresses differently: the main focal area of scaly erythema is the skin folds: groin, elbow folds, skin fold, on the neck. The papules are itchy, children are constantly tormented, irritable and irritable. Overall, all of the clinical variations observed in children are similar to those observed in adults. The difference relates to the complete manifestations, the location of the pathological process and the course of the disease.
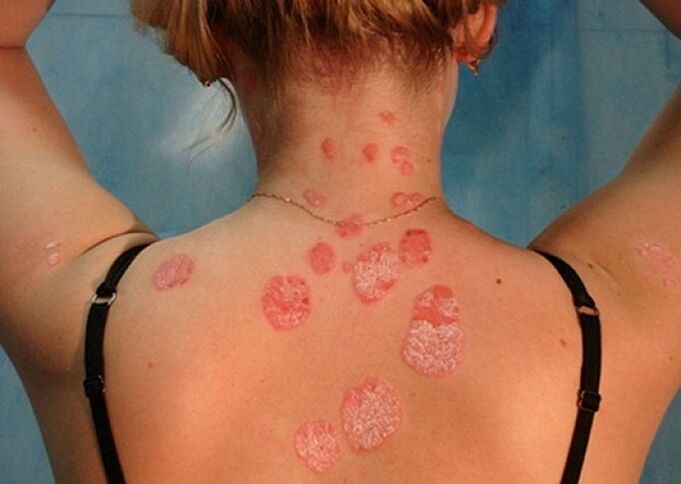
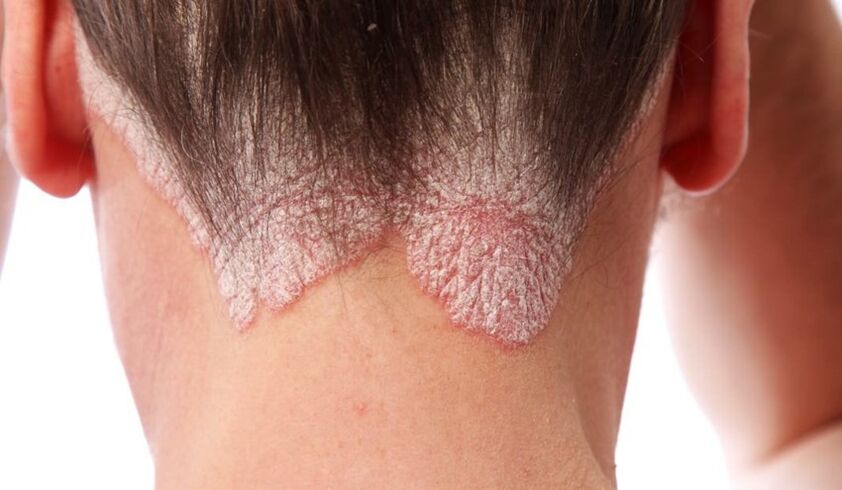
4 stages of psoriasis
Clinical dermatology, based on the difference in symptoms, extent of skin damage and duration, distinguishes three stages of the psoriasis process. However, it is argued that the early stage must be seen as another formal stage in the development of the disease.
- Initial stage.The first sign of a psoriatic lesion is a small rash. The sites of their occurrence can be different and depend on the type of disease. Primary papules are not more than 3 mm in size, painted in light pink color, after 3-4 days are replaced with a gray spot - dead dermis granules form in place. This process is accompanied by itching and burning, and the general health worsens. In general, the formation of plaques in the early stage takes up to three weeks, and at this time a person has a chance of slowing down the development of the pathology.
- Progressive.At this stage, the disease affects significant areas of the skin: for example, with common psoriasis, plaques are formed, with other forms being their characteristic papules. During the development of the disease, individual spots fuse together, covered with a gray scaly layer. The symptom for which a progressive stage is identified is the Köbner phenomenon (isosceles reaction). All lesions on the skin over time are accompanied by the appearance of psoriatic papules in this area. Another confirmation that the disease is actively developing is the appearance of blood droplets, similar to dew, after the removal of plaque. The duration of this stage depends on the type of lesion. It takes an average of two weeks to two months.
- Stationary stage.During this period, a thick gray-white or gray crust forms. The pink rims disappear. The skin becomes rough, the dry particles are continuously exfoliated from there. The itching and burning sensation becomes less of a discomfort, but it doesn't go away completely. New papules are not formed. This stage can be quite long.
- Depression period.The final stage of the development of the disease, in which there is a gradual decrease and reabsorption of plaques. Itching is no longer bothersome. A clear sign of regression is a symptom of Voronov, when the papules are surrounded by white rings. Fading of the spots occurs from the center to the periphery, so strange patterns form on the skin. Towards the end of the regression, only areas of skin that are slightly different in color from the healthy area will be reminiscent of psoriasis. There is no need to talk about full recovery in the case of psoriasis. The last stage of the regressive phase shows that the cycle of the disease is complete, and can return at any time. For prolonged remission, it is necessary to pay attention to health: avoid provoking factors, carry out a diet, follow up with a dermatologist.
Psoriasis examination plan
- General clinical analysis of blood.
- Research on the content of vitamins D, B12, folic acid in the blood.
- Blood test looks for ALT (alanin aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, cholesterol with lipid profile, creatinine, glucose, insulin, total protein.
- Blood for rheumatoid factor, c-reactive protein, uric acid, ASLO.
- Ferritin, transferrin, serum iron are indicators of anemia (especially chronic diseases).
- Thyroid control panel: TSH, T4 sv, TK sv.
- Reproduced programs.
- KhMS according to Osipov.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Traditional treatments for psoriasis
Early therapy.
The sooner a person discovers the first signs of skin damage see a doctor, the more chances are that the more timely measures can be taken to stop the rapid development of the disease and transition to a chronic form -and thus, the overall standard of living would be greatly improved.

One of the drugs that are often prescribed for an onset of illness is salicylic ointment. It has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects, has a keratolytic effect, so that the plaques are eliminated of the keratinized particles. For the relief of itching, naphthalan ointment is also used.
Therapy in an advanced stage.
At this stage, a comprehensive treatment is required and can only be provided by an experienced specialist. Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms, eliminating toxins from the body. To normalize metabolism, intramuscular injection of calcium gluconate is usually prescribed. Sodium thiosulfate reduces inflammation and eliminates the manifestations of intoxication.
To moisturize the inflamed areas of the skin, a special emulsion and salicylic ointment are used. Tarot-containing drugs are contraindicated in an advanced stage: they have an unpleasant and painful effect on the patient.
When the intensity of inflammation decreases, physiotherapeutic procedures may be connected. Psoriasis patients are exposed to ultraviolet radiation, PUVA therapy and paraffin topical. Corticosteroids and cytostatics are not used unnecessarily, these powerful drugs are needed only in difficult and severe cases.
To reduce allergic manifestations, antihistamines are prescribed and sedatives are prescribed to relieve stress. Diuretics help reduce swelling in the inflamed skin and remove toxins from the body.
Stationery therapy.
At this stage, the inflammation fades, the plaques become covered with a dry crust, so funds are needed to alleviate the discomfort caused by the appearance of a scab. These are tar shampoos, oil-based emulsions.
In many patients, ultraviolet irradiation and PUVA technique are effective. If there is no improvement, the doctor prescribes cytostatics.
Therapy in the regressive stage.
In the late stages of the cycle of the disease, it is necessary to constantly adjust treatment methods, depending on the patient's current condition. Prevention is replacing positive therapeutic actions.
The patient receives recommendations for dietary and lifestyle changes in general. To avoid reintegration of the skin, avoid stressful situations that cause psoriatic plaques to form.
Usually, doctors give their patients the following advice:
- review of lifestyle: adjust the diet, get enough sleep, be more active;
- ensure normal vitamin levelsD, iron, vitamin B, protein in the body;
- normalize the digestive tract: elimination of acid depletion, impaired bile flow, SIBO and CIGR (syndrome of excessive bacteria and, consequently, fungal growth);
- get rid of the foci of chronic infection: oral hygiene, treatment with ENT doctor;
- deal with concomitant somatic pathologies: hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, etc. v.
Traditional methods to get rid of psoriasis
- Initial stage.At the first signs of skin damage, juniper and lavender oils are effective. They soothe irritated areas of the dermis, promote healing of small wounds, and reduce feelings of tension. A few drops of oil are added to creams with neutral ingredients, such as those intended for children, and applied to the rash. Another popular method to deal with early symptoms of psoriasis is to use 3% hydrogen peroxide. Any remedy, even the most harmless at first glance, can be taken after consulting a dermatologist. Changing your diet, avoiding unhealthy foods and alcohol are also common recommendations among traditional healers.
- Progressive stage.At the rapidly developing stage of the disease, the cormorant infusion is added to the healing oil and hydrogen peroxide. To prepare it you will need fresh or dry stalks and brine. Alcohol drugs are contraindicated, they can aggravate the condition of the affected skin area. It is necessary to press the cineraria for at least a few hours and before applying the healing solution to the plaques, treat them with black birch.
- Stationary stage.At the cessation of new papillae, you can use proven folk remedies that are sure to not harm the sick person. These include the use of sulfuric ointment, salicylic solution.
- Depression period.In the late stages of the disease, hirudotherapy is often used. Although this method is not officially recognized by traditional medicine, many experts have not ruled out its effectiveness. The procedures are performed within 3 - 10 days, depending on the patient's health condition.

Psoriasis prevention: how to prevent the development of the disease
- Skin Care.To minimize the likelihood of psoriasis damage from a genetic predisposition, simple ways to maintain skin health help: water and skin care procedures (bathing, bathing with herbal extractsand salt, contrast shower, soak in cool air in the air, etc. ); use a soft sponge and avoid hard towels that could damage the skin; the use of detergents, which have natural ingredients, do not have strong chemical ingredients.
- Ultraviolet ray.Several studies have demonstrated the beneficial effects of sun exposure on skin prone to psoriasis. Moderate UV light helps to speed up tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation. You should not overdo sunbathing: too much rays can worsen the disease.
- Clothes.Synthetic fabrics, tight-fitting pants, multiple belts and laces - all of these are contraindicated for patients with psoriasis, even in remission. Clothing should be natural, hypoallergenic, loose-fitting, without any inconvenience that could lead to visible symptoms returning. Dark tones should be avoided for cosmetic reasons; Silver-white scales are less visible on light-colored clothing.
- Injured.In the patient with psoriasis, any small wound, abrasion, or abrasion can cause a return of progression and secondary infection in the skin. They must be extremely careful to avoid injury.
- Cosmetic and household products.Not all remedies are appropriate to maintain cleanliness for people with such a diagnosis. When choosing shower gel, soap, shampoo, it is important to pay attention to their ingredients, preferring those that contain natural ingredients. It is better to buy the wide range of therapeutic care products sold in pharmacies. Absolutely contraindicated to exfoliants with solid ingredients: they can restart the course of the disease due to the smallest lesions on the skin. Household chemicals should also be selected based on safety, do not use strong chlorine and alkaline cleaning powders. Gloves should be worn when cleaning to avoid adverse effects on the skin of the hands.
- Vitamin therapy.Maintaining the balance of vitamins is indicated for everyone, and especially for people with chronic dermatitis. Complex preparations keep the body in good condition, help it fight off viruses and prevent metabolic disorders.

Psoriasis- This is not a death sentence, but a very serious reason to reconsider the rules you lived in before. Your allies on the path to overcoming illness should be qualified specialists - dermatologists, nutritionists, therapists. With their help, as well as through deliberate treatment, you can learn to live comfortably, regardless of your diagnosis.